
- #Creating Dynamic Blocks In Autocad Software Are Helpful
- #Creating Dynamic Blocks In Autocad How To Use Them
- #Creating Dynamic Blocks In Autocad Trial Art Extensively
Creating Dynamic Blocks In Autocad Software Are Helpful
The term CADD (for c omputer aided design and drafting) is also used. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. While it does take a little more time up front to create a dynamic block, the timesavings on the back end are well worth the effort Even better news: if you are a proficient user of AutoCAD software, you should have no problem converting those boring, static Computer-aided design ( CAD) is the use of computers (or workstations) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. Why should you be using Dynamic Blocks Quite simply, Dynamic Blocks can greatly reduce the number of blocks in your library, improving your efficiency.
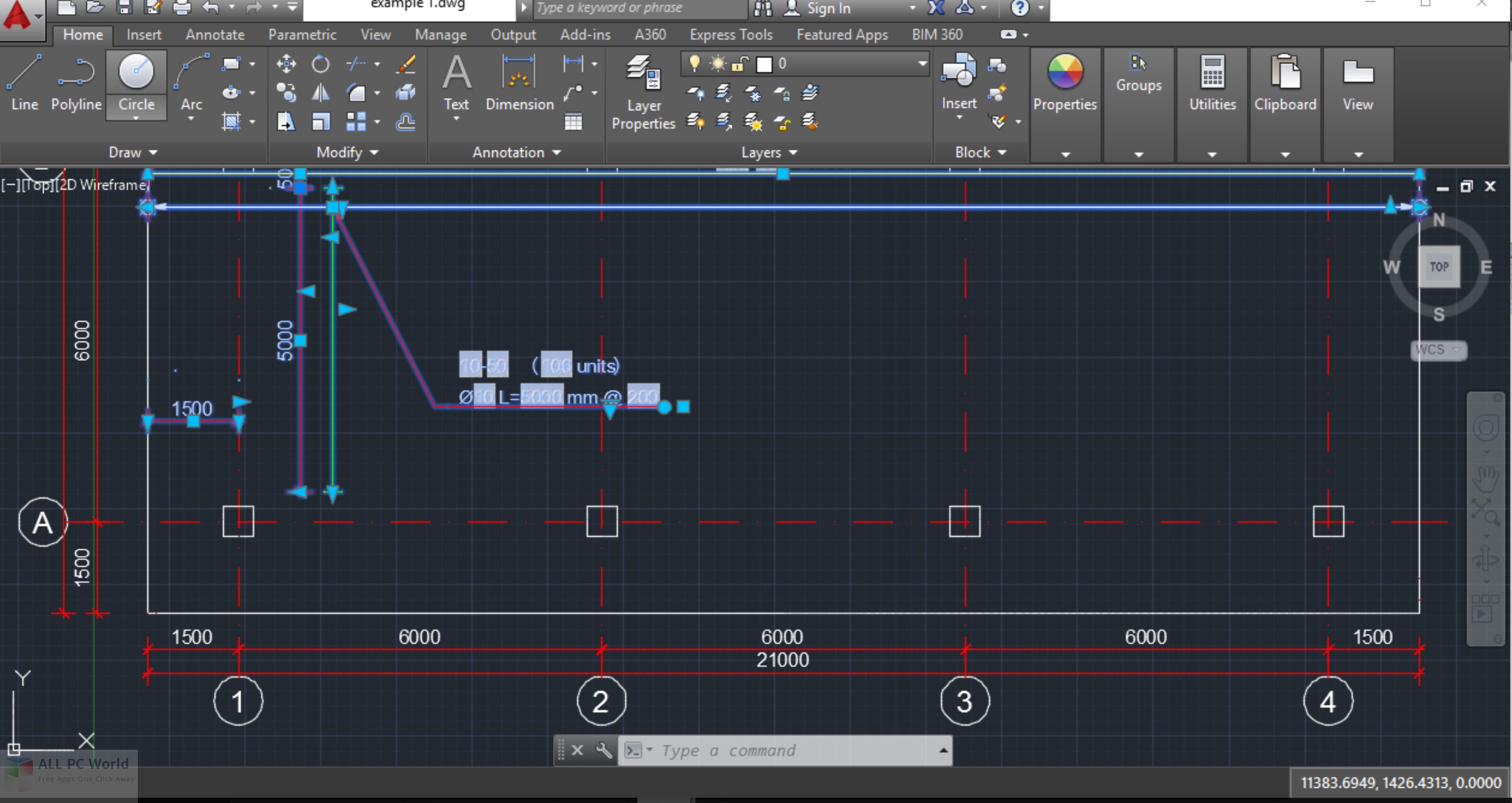
In mechanical design it is known as mechanical design automation ( MDA) or computer-aided drafting ( CAD), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. 2020Its use in designing electronic systems is known as electronic design automation ( EDA). A Dynamic block allows you to dynamically change 2D Objects in various ways, like rotate, scale, move, show or hide.20 fv. I mostly use this feature to create dynamic symbols that can be used in drawings, like Section arrows, 2D Pipe ends, North Arrows, etc.
Creating Dynamic Blocks In Autocad Trial Art Extensively
CAD is also widely used to produce computer animation for special effects in movies, advertising and technical manuals, often called DCC digital content creation. CAD is an important industrial art extensively used in many applications, including automotive, shipbuilding, and aerospace industries, industrial and architectural design, prosthetics, and many more. As in the manual drafting of technical and engineering drawings, the output of CAD must convey information, such as materials, processes, dimensions, and tolerances, according to application-specific conventions.CAD may be used to design curves and figures in two-dimensional (2D) space or curves, surfaces, and solids in three-dimensional (3D) space. However, it involves more than just shapes. But have you ever tried making dynamic blocks Dynamic blocks have the capabilities to stretch, flip, rotate, or move.CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics to depict the objects of traditional drafting, or may also produce raster graphics showing the overall appearance of designed objects.
Some CAD software is capable of dynamic mathematical modeling.CAD technology is used in the design of tools and machinery and in the drafting and design of all types of buildings, from small residential types (houses) to the largest commercial and industrial structures (hospitals and factories). Modern CAD packages can also frequently allow rotations in three dimensions, allowing viewing of a designed object from any desired angle, even from the inside looking out. CAD is an example of the pervasive effect computers were beginning to have on the industry.Current computer-aided design software packages range from 2D vector-based drafting systems to 3D solid and surface modelers. It did not eliminate departments as much as it merged departments and empowered draftsmen, designers, and engineers. CAD was a revolutionary change in the engineering industry, where draftsmen, designers, and engineering roles begin to merge. During this transition, calculations were still performed either by hand or by those individuals who could run computer programs.
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. CAD enables designers to layout and develop work on screen, print it out and save it for future editing, saving time on their drawings.This section does not cite any sources. 4D BIM is a type of virtual construction engineering simulation incorporating time or schedule-related information for project management.CAD has become an especially important technology within the scope of computer-aided technologies, with benefits such as lower product development costs and a greatly shortened design cycle. Furthermore, many CAD applications now offer advanced rendering and animation capabilities so engineers can better visualize their product designs. It can also be used to design objects such as jewelry, furniture, appliances, etc.
Potential blockage of view corridors and shadow studies are also frequently analyzed through the use of CAD. Document management and revision control using product data management (PDM)CAD is also used for the accurate creation of photo simulations that are often required in the preparation of environmental impact reports, in which computer-aided designs of intended buildings are superimposed into photographs of existing environments to represent what that locale will be like, where the proposed facilities are allowed to be built. Photorealistic rendering and motion simulation. Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) including instructions to computer numerical control (CNC) machines Computer-aided engineering (CAE) and finite element analysis (FEA, FEM)
Creating Dynamic Blocks In Autocad How To Use Them
These provide an approach to the drawing process without all the fuss over scale and placement on the drawing sheet that accompanied hand drafting since these can be adjusted as required during the creation of the final draft.3D wireframe is basically an extension of 2D drafting (not often used today). Also its stress, strain, timing, or how the element gets affected in certain temperatures, etc.See also: Comparison of computer-aided design editorsThere are several different types of CAD, each requiring the operator to think differently about how to use them and design their virtual components in a different manner for each.There are many producers of the lower-end 2D systems, including a number of free and open-source programs. The features in the CAD system can be used for the variety of tools for measurement such as tensile strength, yield strength, electrical, or electromagnetic properties. Parameters and constraints can be used to determine the size, shape, and other properties of the different modeling elements. The construction history can be used to look back into the model's personal features and work on the single area rather than the whole model. Using four properties which are history, features, parameterization, and high-level constraints.
Parametric modeling allows the operator to use what is referred to as "design intent". Basic 3D solids don't usually includes tools to easily allow the motion of the components, set there limits to their motion, or identify interference between components. Two-dimensional projected views can easily be generated from the models. Basic three-dimensional geometric forms (prisms, cylinders, spheres, rectangle) have solid volumes added or subtracted from them as if assembling or cutting real-world objects. The operator approaches these in a similar fashion to the 2D systems, although many 3D systems allow using the wireframe model to make the final engineering drawing views.3D "dumb" solids are created in a way analogous to manipulations of real-world objects (not often used today). The final product has no mass properties associated with it and cannot have features directly add to it, such as holes.
As with parametric modeling, direct modeling has the ability to include the relationships between selected geometry (e.g. Direct or explicit modeling provide the ability to edit geometry without a history tree With direct modeling, once a sketch is used to create geometry the sketch is incorporated into the new geometry and the designer just modifies the geometry without needing the original sketch. If the operator designs the part as it functions the parametric modeler is able to make changes to the part while maintaining geometric and functional relationships. The feature could be located using any geometric object already available in the part, but this random placement would defeat the design intent. If a feature was intended to be located from the center of the part, the operator should locate it from the center of the model. Any future modifications can be made by changing on how the original part was created.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
